Sending "1byte" data - I2C bus
- Tasnemul Hasan Nehal
- Nov 17, 2020
- 2 min read
Objective:
Here we will learn how to establish a I2C bus serial communication between 2 Arduinos and how a Slave Arduino can send "1byte" of data (ex: 0x47) to the Master Arduino.
Theory:
Before we go for coding, we must know the basics of I2C bus and how it works. I highly recommend you to go through Scott Campbell's article on I2C bus to understand it better.
Hardware Setup:
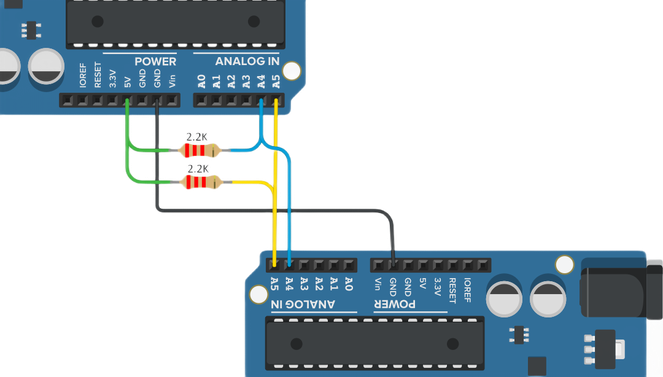
Full Code:
ArduinoA (Master)
#include<Wire.h> //the main library
byte x; //the incoming data will be stored here
void setup()
{
Wire.begin(); //only for master to create communication
Serial.begin(9600); //MCU & Serial Monitor communication starts
}
void loop()
{
Wire.requestFrom(0x52, 1) //requesting data from Slave
while(Wire.available() > 0)
{
x =Wire.read(); //reads incoming dat byte
Serial.println(x, HEX);
}
}ArduinoB (Slave)
#include<Wire.h> //the main library
void setup()
{
Wire.begin(0x52); //slave address to call by Master
Serial.begin(9600); //MCU & Serial Monitor communication starts
Wire.onRequest(sendData);
}
void loop()
{
;
}
void sendData()
{
Wire.write(0x47); //sending data at request
}Code Explanation:
At Master
Wire.requestFrom(0x52, 1);Requesting Slave no-0x52 send 1byte data
byte n = Wire.requestFrom(0x52, 1);Requesting Slave no-0x52 send 1byte data. If the slave 0x52 is online on the bus, then n=1, not necessary any data to come. This value "1" is used to allocate memory space for incoming data.
byte n = Wire.requestFrom(0x52, 5);Here n=5. Which means the Master allocated 5 bytes of data where incoming data will be stored. Now if 2/3 bytes data comes then the rest of the memory location will be auto-filled with 0xFF (in decimal = 255)
while( Wire.available() > 0 ) Till there are data coming from Slave/data is available to receive, this loop will run to receive & store incoming data.
Serial.println(x, HEX); print 1 byte in hexadecimal form (0x47), without HEX it would be a Decimal value (71)
At Slave
Wire.onRequest(sendData); When the Master asks to send any data by terminating "Wire.requestFrom(0x52, 1)" in the Master side code, the "sendData" function will run automatically to send the requested data. This function works only for Slaves. Masters dont have this type of sending function. "sendData" is a regular function name, it can be replaced by any name that follows the Variable naming rules.
Result:
Master's Serial Monitor

See More Examples:


Comments